DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
Your car has been misbehaving of late. Somehow she just doesn't seem to perform like she did in the past. It is very likely that there is a problem with your car and that she already threw an error code, now stored in its OBD (on-board Diagnostics) system. Fortunately this stored data can be retrieved via the diagnosis interface because diagnostic error codes have been standardized globally. Implying that the stored data can be retrieved with any Generic Scan Tool. Virtually every VW service center and even some private mechanics have one or more. Many private individuals have also invested in scan tools because automotive repair cost have just skyrocketed of late hence they prefer to do the repairs themselves. I've been doing all my VW repairs for the past 8 years.OK, so now that youv'e done a diagnostic scan of your car, and retrieved the diagnostic scan codes, the printout looks like a foreign language. You desperately need help to understand what it means but you are no nearer to solving the misbehaving problem with the scan in hand, than you were without the scan. Don't worry, after explaining the basics of scan analysis, you will have a decent idea how to interpret your particular scan and perhaps even do the repair yourself before deleting / clearing the error code.
 |
| Low cost Diagnostic scan tools from various manufacturers. |
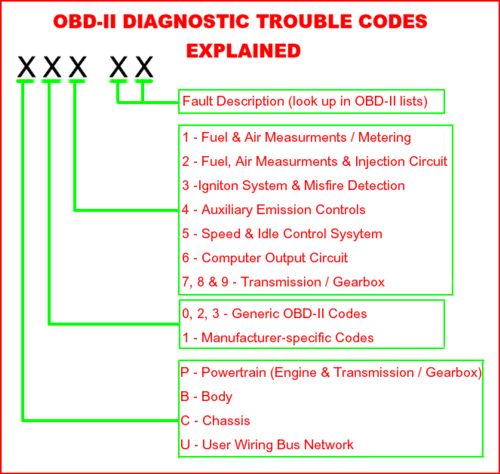
Before we start to analyse the scan there are a few things that I need to mention. Diagnostic errors or more correctly DTC (diagnostic trouble codes) are numerous and fall into to categories, viz Generic fault codes / manufacturer-specific fault codes. However, there is a third category specific to VAG vehicles, though many mechanics also consider them as manufacturer-specific. But I will expound on this later. Fault code are divided into four categories viz, P, B, C and U One of these four alphabetical letters always precede four numerals and are thus referred to as an alphanumeric code or just code for short. The P category is by far the most interesting. Both Generic fault codes and manufacturer-specific fault codes are applicable to all OBD-II vehicles but manufacturer-specific fault code definitions vary from manufacturer to manufacturer and are also different to VAG codes.
P CODES
The P stands for powertrain, meaning the car's engine and gearbox / transmission. So any and all preceded by a P is associated with engine or transmission problems. For example, P0100 is a powertrain code that correlates to 'mass air flow circuit problem'. P0200 is also a powertrain code that correlates to an 'open circuit injector'. P0300 is a another powertrain code that correlates to the 'detection of random/multiple cylinder misfires'. P codes start at P0000 and range to P3999. Generic P codes are a subset of P codes and start with either P0xxx, P2xxx and P34xx - P39xx, implying that P codes staring at P1xxx and P30xx- P33xx are not generic but manufacturer-specific codes.As can be seen above, in the Powertrain system , the first digit after the P indicates whether or not the code is generic or manufacturer-specific. The second digit identifies a specific area of the vehicle that's at fault. The powertrain components are divided into 9 distinct area as can be seen below. ( Refer to diagram below)
1xx Fault codes related to 'Fuel & Air Metering'
2xx Fault codes related to 'Fuel, Air metering & Injection Circuit'
3xx Fault codes related to 'Ignition System & Misfire Detection'
4xx Fault codes related to 'Auxiliary Emission Controls'
5xx Fault codes related to 'Vehicle Speed & Idle Control System'
6xx Fault codes related to 'Computer Output Circuit'
7xx Fault codes related to 'Transmission / gearbox related faults'
8xx Fault codes related to 'Transmission / gearbox related faults'
9xx Fault codes related to 'Transmission / gearbox related faults'
The third and fourth digits identify the specific component involved with the fault. This can be referenced from a complete list of codes that can be downloaded from various OBD sites. For example, www.outilsobdfacile.com/ www.obd-codes.com/trouble_codes/ www.launchtech.co.uk www.trouble-codes.com/ www.automotive-technology.co.uk
The fault code doesn't identify the actual component that's causing the fault but rather narrows it down the area that needs to be investigated. Often times the sensor that does the detection actually goes faulty. For instance, the crankshaft position sensor and camshaft position sensors are prone to failure, causing the engine to stall or fail to start.
 |
| OBD-II Diagnostic Trouble Codes Explained |
B CODES
B stands for Body and includes the Air Bag and other mechanical / electronic components not associated with the engine and transmission/gearbox. For example, B0005 is a body error code and correlates to a 'park switch circuit malfunction'. B0530 is another body error code and correlates to a 'stuck fuel level sensor'. Generic body trouble codes start with either B0xxx or B3xxx, again implying that B codes starting with B1xxx and B2xx are manufacturer-specific codes.C CODES
C stands for Chassis and include the ABS and other mechanical / electronic components not associated with neither the engine and gearbox nor the body. For example, C0281 is a chassis error code and correlates to a 'brake switch circuit malfunction'. C0238 is a chassis error code and correlates to a 'wheel speed mismatch'. The generic network trouble codes for C start with either C0xxx or C3xxx. C codes starting with either C1xxx or C2xxx are manufacturer-specific codes.U CODES
U stands for User Network. Initially the U stood for “undefined” but is now network-related. For example, U0109 is a network error code and correlates to 'lost communication with fuel pump control module'. U0405 is another is a network error code and correlates to 'invalid data received from cruise control module'. The generic network trouble codes for U start with either U0xxx and or U3xxx, again implying that codes starting with U1xxx and U2xxx are manufacturer-specific codes.VAG CODES
Now VAG codes on the other hand range from 00000-65535 and don't have any letters. It is just a 5 digit numeral and coincides with the list of both generic code and manufacturer specific codes. For example:-VAG code 16385 coincides with generic code P0001 - Fuel Volume Regulator Control Circuit Open
VAG code 16389 coincides with generic code P0005 - Fuel Shutoff Valve (A) Circuit Open
VAG code 16434 coincides with generic code P0050 - Oxygen Sensor Heater Bank 1/2 Control Circuit
Generic fault code P0403 equates to a VAG 16787 - EGR Valve Malfunction
Generic fault code P0571 equates to a VAG 16955 code - Brake Switch Signal Implausible
Generic fault code P1690 equates to a VAG 18098 code - Malfunction Indication Light (K83)
Generic fault code P1814 equates to a VAG 18222 - Transmission Pressure Control Valve open or Short to Ground
Generic fault code P0032 equates to a VAG 000050 - Oxygen (Lambda) Sensor Heating Circuit Short to Plus
Generic fault code P0720 equates to a VAG 17104 - Transmission Output Speed Sensor (G195) Circuit Malfunction
Generic fault code P1517 equates to a VAG 17925 - ECU Power Supply Relay Malfunction
Address 17: Instruments Labels: Redir Fail!
Part No: 6Q0 920 820 H
Component: KOMBI+WEGFAHRSP VDO V05
Coding: 00141
6 Faults Found:
01312 - Powertrain Data Bus
37-10 - Faulty - Intermittent
01314 - Engine Control Module
49-10 - No Communications - Intermittent
01316 - ABS Control Module
49-10 - No Communications - Intermittent
01321 - Control Module for Airbags (J234)
49-10 - No Communications - Intermittent
01322 - Control Module for Multi-Function Unit (MFA) (J501)
49-10 - No Communications - Intermittent
01309 - Power Steering Control Module (J500)
49-10 - No Communications - Intermittent
The clipping below displays both generic and VAG error codes as well as a fault description in number code.
Address 01: Engine Labels: 06A-906-032-BBW.lbl
Part No: 06A 906 032 RJ
Component: 2.0l R4/2V G 6505
Coding: 00003
4 Faults Found:
17837 - Circuit for Brake Vacuum Pump
P1429 - 35-00 - Open Circuit
16452 - MAP/MAF Throttle Position Correlation
P0068 - 35-00 -
16804 - Catalyst System; Bank 1
P0420 - 35-00 - Efficiency Below Threshold
16395 - Bank 1: Camshaft A (Intake)
P0011 - 35-10 - Retard Set point not Reached - Intermittent
The clipping below shows VAG 5 digit codes and description numbers.
46 Address: Central Conv. Labels: 1C0-959-799.lbl
Part No: 1C0 959 799 C
Component: HLO Komfortgerát 1H 0003
Coding: 00258
3 Faults Found:
01330 - Central Control Module for Central Convenience (J393)
53-10 - Supply Voltage Too Low - Intermittent
00849 - S-contact at Ignition / Starter Switch (D)
25-00 - Unknown Condition Switch
01359 - Internal Central Locking Switch; Passenger Side (E198)
27-10 - Implausible Signal - Intermittent
As can be seen in two of the examples above, there are also numbers like, 27-10, 37-10, 49-10, etc. The first two digits of each set of numbers are the numeric equivalent to the text meaning 'Implausible Signal, 'Faulty and 'No Communications' respectively. Each set of numbers ends in -10, which means 'intermittent'. Hence 27-10 means Implausible Signal - Intermittent, 37-10 means Faulty - Intermittent and 49-10 means No Communications - Intermittent. Fault codes can also have a -00 suffix in place of -10 which implies a definite fault (not intermittent). Occasionally you would encounter just a hyphen (-). This implies that the scan equipment could not retrieve further details about the fault and just left it blank.





