Volkswagen and Audi EPC
The Internet is a huge repository of information, some useful and some not so useful, or more to the point, useless. But, there is so much of both, duplicated and reechoed in posts like auto-facts, axleaddict, youfixcars, and motor forums by so many individuals. There is nothing worst than being led up the garden path by some ignoramus who knows squat about electro-mechanical engineering technology when you are desperately looking for answers. To reduce that from happening, I decides to bust some of the myths related to VAG cars that are being echoed over and over and over.EPC can be a bitch to repair.
Myth 1Here's the first myth from someone on Yahoo Answers, relating to a 2012 VW Polo. "You can clear fault codes by disconnecting your battery for a while". And here's another, "just disconnect the battery on your Audi A3 for a little more than 10 seconds and your fault codes will be gone"!
Myth 1 Busted
Though the above is true for pre-1996 vehicles fitted with OBD-I, disconnecting the battery on any car manufactured post-1996 fitted with OBD-II will definitely not delete any fault codes because the ECU stores all DTC (Dignostic Trouble Codes) aka fault codes codes in its non-volatile memory. What it will do, is reset the cpu / timer. The term non-volatile memory is generally used for all types of solid state memory, meaning memory that doesn't need its contents refreshed periodically.
However, the ECU also stores learnt values and basic settings, like for example the Fuel Control Learning Adaptation Values and the Kick-Down Position of the Accelerator which is needed by the automatic transmission. This data and your car's radio code is not stored in non-volatile memory and will undoubtedly be erased when the battery is disconnected. Once the battery is reconnected, the adaptation process needs to be done which will enable the ECM to learn the new settings for the Drive-by-Wire electronic throttle valve and store it. If you didn't save the radio code you have to go to a VW / Audi dealer with your VIN and they may be able to give it to you.
When you disconnect your car's battery, the ECU detects the loss of battery power and registers a DTC in the ECU's non-volatile memory to that effect. This record can be seen after the battery is reconnected and a diagnostic scan is performed. It would look something like this,
2 Faults Found:
00532 - Supply Voltage B+
07-10 - Signal too Low - Intermittent
01598 - Drive Battery Voltage
07-10 - Signal too Low - Intermittent
Removing the negative terminal of the battery isn't all bad, it does have the advantage of resetting the system's ECU safety watchdog timer. A safety watchdog timer (WDT) is responsible for periodically generating a system reset in the event of a software glitch. This one of a kind CIC61508 safety watchdog timer is ASIL-D (Automotive Safety Integrity Level D) approved, where level D refers to the highest classification of initial hazard against the risk of injury as defined within ISO26262 automotive industry standard.
 |
| Infineon Safety Watchdog timer |
Pressure Sensors
Myth 2
There are pressure sensor in the VW and Audi engine block that causes an EPC light to come on and make the car go into limp mode.
Myth 2 bustedYes, there are pressure sensors in both VW and Audi engines but they not fitted into the block and should not be mistaken for than for knock senors that are screwed to the block. Faulty or loose knock sensors can cause the EPC light to come on and send the car into limp mode. The baro sensor measures the ambient air pressure and has a effect on engine performance altitude dependent. The supercharger boost pressure is controlled via the regulating flap control unit Intake manifold pressure sensor/MAP sensor (MAP = Manifold Air Pressure) which can cause the EPC light to come on and send the car into limp mode. The high-pressure fuel pump delivers fuel at a pressure of up to 150 bar and any drop in this pressure can cause the EPC light to come on and send the car into limp mode. Common problem with loss of pressure is the fuel filter. Loss of oil pressure can cause the EPC light to come on and send the car into limp mode. Lastly there is high system pressure in the cooling system at high revs and sudden loss of this pressure can cause the EPC light to come on and send the car into limp mode.
Myth 3
EPC light usually means that the Electronic Throttle Body needs replacing and reprogramming.
Myth 3 busted It is advantages to perform adaptation on the throttle body, before attempting to replace it with a new throttle body . Often times replacing it makes no difference and normally turn out to be the wiring harness connectors to the throttle body that's defective. Disassemble the three electrical connectors around the throttle body clean this inside of the connectors with circuit cleaner and reassembled. Also check for vacuum leaks, especially pressure regulator hose and the small pipes connected to the intake-manifold before replacing anything.
Myth 4
Epc light is mostly known to come on when there is emissions problems.
Myth 4 busted This is incorrect because the 'check engine light' is specific to emission related problems, however The EPC light may also come on if the emission related problem affects the engine torque. So repairing the emission related problem first would in most cases reset both the EPC light and the 'check engine light'.
Sensors associated with EPC
Extensive safety measures have been designed and implimentedin both the hardware and software of Audi and VW. In most cases dual sensors are used for continual self-checking of signal plausibility. A safety watcg dog timer is integrated in the Motronic ECM to constantly and continually monitor the processor for correct and proper operation. Some of the sensors are listed below.
Fuel Pressure Sensor G247
Low Fuel Pressure Sensor G410
Oil Level Thermal Sensor G266
Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) G39
Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) 2 G108
Oxygen Sensor (O2S) G130 & G130
situated behind 3 Way Catalytic Converter (TWC) G130
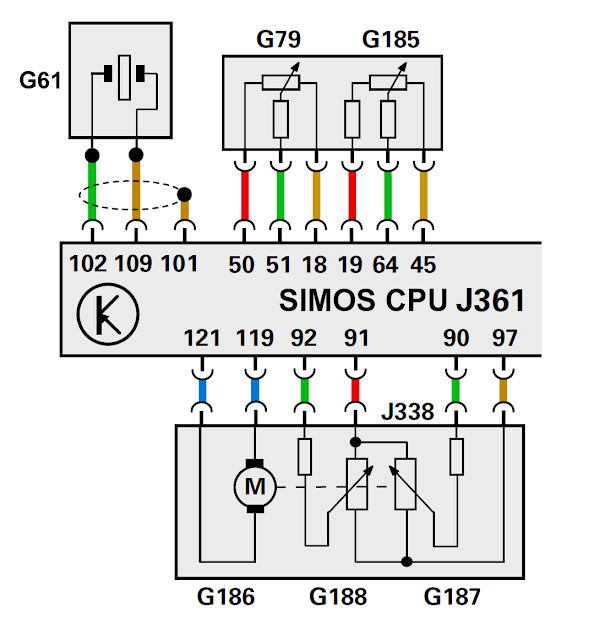
G186 Throttle Drive (EPC))
G187 Throttle Drive Angle Sensor 1 (EPC))
G188 Throttle Drive Angle Sensor 2 (EPC))
Engine Speed (RPM) Sensor G28
Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor G70
Throttle Position (TP) Sensor G79
Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor 2 G185
Clutch Position Sensor G476
Throttle Valve Control Module J338
Throttle Drive Angle Sensor 1 (EPC) G187
Throttle Drive Angle Sensor 2 (EPC) G188
Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor G40
Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor 2 G163
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor G62
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor G83 (on radiator)
Knock Sensor (KS) 1 G61
Knock Sensor (KS) 2 G66
Brake Light Switch F